Imagine a world where plants grow without soil, using only water and nutrients. Sounds intriguing, doesn’t it? That’s exactly what hydroponic farming is all about. In this article, we will explore the various benefits and challenges associated with this innovative method of growing plants. From increased yields and water conservation to the potential for year-round cultivation, hydroponic farming holds immense promise for the future of agriculture. However, it also comes with its fair share of challenges, such as the initial setup costs and the need for precise monitoring. So buckle up and get ready to dive into the fascinating world of hydroponic farming!
Increased Crop Yield
Optimal Nutrient Delivery
Hydroponic farming allows for optimal delivery of nutrients to plants. Instead of relying on soil for nutrient uptake, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, ensuring that they receive all the essential elements they need for growth. This precise control over nutrient delivery results in healthier, more vigorous plants that can produce higher yields.
Controlled Environment
One of the key advantages of hydroponic farming is the ability to create a controlled environment for plants. By carefully monitoring and adjusting factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, farmers can provide the ideal conditions for plant growth. This controlled environment minimizes stress on the plants, allowing them to allocate more energy towards producing crops. As a result, hydroponic systems often yield higher crop productivity compared to conventional farming methods.
Year-round Crop Production
Hydroponic farming also enables year-round crop production. Unlike traditional agricultural practices that are limited by seasonal changes, hydroponic systems can be set up in any location and operate throughout the year. By utilizing artificial lighting and climate control systems, farmers can ensure that their crops receive the necessary light and warmth even during the winter months. This extended growing season leads to increased crop yields and a more stable food supply.
Water Efficiency
Conservation of Water
Water efficiency is a crucial benefit of hydroponic farming. In traditional agriculture, a significant amount of water is wasted due to evaporation, runoff, and inefficient irrigation practices. In hydroponic systems, water is recirculated and reused, resulting in significantly less water consumption compared to soil-based farming. Additionally, the closed-loop nature of hydroponics ensures that water is used more efficiently, reducing the overall water footprint of agricultural operations.
Reduced Water Pollution
Hydroponic farming can help address the issue of water pollution commonly associated with conventional farming. Chemical fertilizers and pesticides used in traditional agriculture can leach into groundwater and nearby water bodies, causing pollution. In hydroponics, the use of chemical inputs is minimized, if not eliminated entirely. This reduces the risk of water pollution, leading to healthier ecosystems and improved water quality.
Resilience to Drought
Growing crops in hydroponic systems offers increased resilience to drought conditions. As water is carefully and efficiently delivered directly to the plants’ root systems, there is minimal water loss due to evaporation or soil absorption. This efficient water usage ensures that crops can thrive even in regions prone to drought, providing a more reliable food supply in areas with water scarcity.
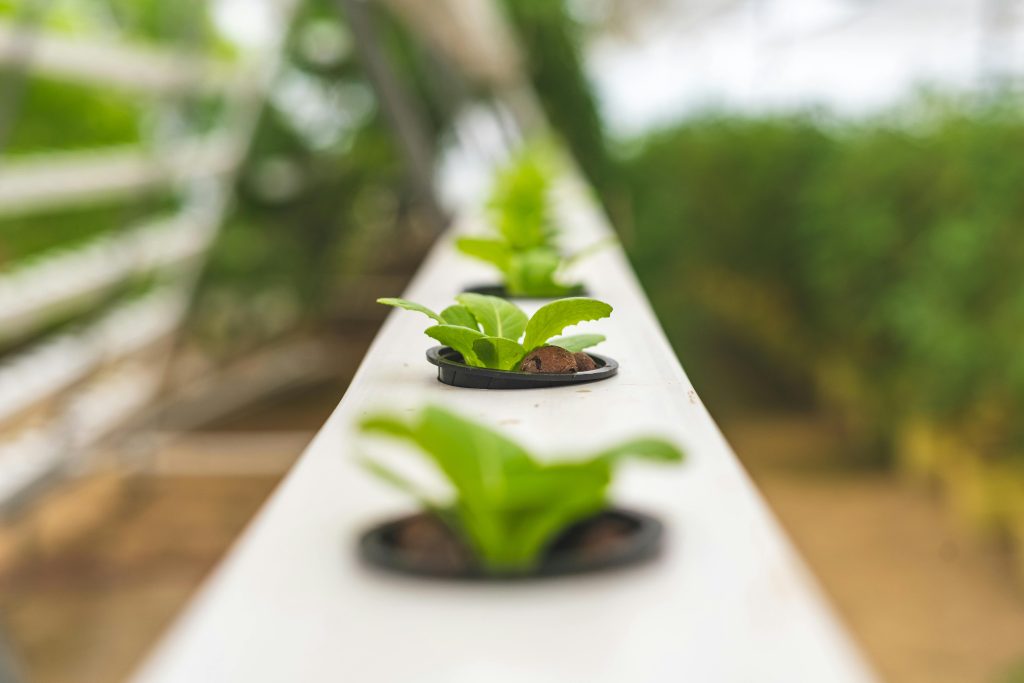

Reduced Space Requirements
Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is a technique commonly employed in hydroponic systems that maximizes space utilization. By growing plants vertically in stacked layers or towers, hydroponic farmers can grow crops in smaller areas compared to traditional farming methods. This vertical arrangement allows for higher plant density, resulting in increased crop yields per unit of land. Vertical farming is particularly beneficial in urban areas, where available land is limited, enabling agriculture to be integrated into city environments.
Utilization of Unused Land
Hydroponic farming also offers the advantage of utilizing otherwise unused or underutilized land. Locations such as abandoned buildings, rooftops, and unused urban spaces can be transformed into productive hydroponic farms. This repurposing of empty areas not only increases food production but also revitalizes neglected spaces, contributing to urban renewal and the creation of green infrastructure.
Increased Crop Density
The controlled environment of hydroponic systems allows for precise and densely packed plant cultivation. With proper spacing and optimal nutrient delivery, plants can be grown closer together without competing for resources. This increased crop density maximizes land usage and leads to higher yields per square foot. By reducing the space requirements for agriculture, hydroponic farming offers a sustainable solution to the growing demand for food in a world with limited arable land.
Elimination of Soil-related Issues
No Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is a significant problem in traditional agriculture, leading to the loss of topsoil, reduced fertility, and environmental degradation. Hydroponic farming eliminates soil erosion altogether since plants are not grown in soil. Instead, they are provided with the necessary nutrients through water-based solutions. This absence of soil erosion helps preserve valuable soil resources and mitigates the negative impacts associated with erosion, such as sedimentation in water bodies and loss of agricultural productivity.
Prevention of Soil Nutrient Depletion
In conventional farming, continuous cultivation and inadequate nutrient management often deplete the soil of essential nutrients. In hydroponic systems, nutrients are supplied directly to the plants’ roots, ensuring that they receive all their required elements. Since there is no reliance on soil for nutrient uptake, hydroponic farming avoids soil depletion, allowing for sustained and efficient plant growth. This eliminates the need for soil amendments and reduces the environmental impact of nutrient runoff.
Absence of Soil-borne Diseases
Plant diseases caused by soil-borne pathogens can have devastating effects on crops and can be challenging to manage in traditional agriculture. However, in hydroponic systems, plants are not in direct contact with soil, reducing the risk of soil-borne disease transmission. This absence of soil-related diseases allows for healthier plants with reduced pest and disease pressure, contributing to higher crop yields and improved overall plant health.

Precise Control over Nutrient Balance
Tailored Plant Nutrition
Hydroponic farming enables farmers to tailor the nutrient composition of the growing solution to meet the specific needs of different crops. By closely monitoring the nutrient levels and adjusting the solution accordingly, plants can receive an optimized balance of nutrients. This precise control over plant nutrition enhances crop growth, development, and overall health, resulting in higher yields and improved crop quality.
Optimized Growth and Development
With hydroponics, farmers have the ability to manipulate environmental factors to optimize plant growth and development. By adjusting parameters such as light intensity, temperature, and humidity, farmers can create conditions that promote optimal growth at various stages of plant development. This fine-tuning allows for faster and more efficient plant maturation, leading to increased crop yields and shortened growing cycles.
Minimization of Fertilizer Use
Hydroponics minimizes the use of fertilizers compared to traditional farming practices. Since nutrients are delivered directly to the plants’ roots, there is no need for excess fertilization that can lead to nutrient runoff and environmental pollution. With precise control over nutrient balance, hydroponic systems can maximize nutrient absorption by plants, minimizing wastage and reducing fertilizer reliance, resulting in cost savings for farmers and a more sustainable agriculture system.
Reduction in Chemical Usage
Elimination of Pesticide Usage
One of the significant benefits of hydroponic farming is the elimination or significant reduction in the use of pesticides. By growing plants in a controlled environment and providing optimal growing conditions, hydroponics naturally reduces the risk of pest infestations. Additionally, the absence of soil-borne diseases further reduces the need for chemical pest control measures. This reduction in pesticide usage leads to safer and healthier food production, minimizing chemical residues and their potential impacts on human health and the environment.
Limited Herbicide Utilization
Weed management is another area where hydroponic farming excels. Without soil, traditional weed pressure is significantly reduced in hydroponic systems. The absence of weeds eliminates the need for herbicides or manual weed removal methods. This reduction in herbicide utilization contributes to more sustainable farming practices, with fewer chemical inputs in the agricultural system.
Closed System Minimizes Runoff
Hydroponic systems are designed as closed-loop systems, meaning that water and nutrients are recirculated and reused rather than being lost to the environment. This closed-loop approach minimizes the potential for nutrient runoff into water bodies, reducing the risk of water pollution. By retaining water and nutrients within the system, hydroponics provides a more environmentally friendly and efficient farming method that minimizes chemical runoff.
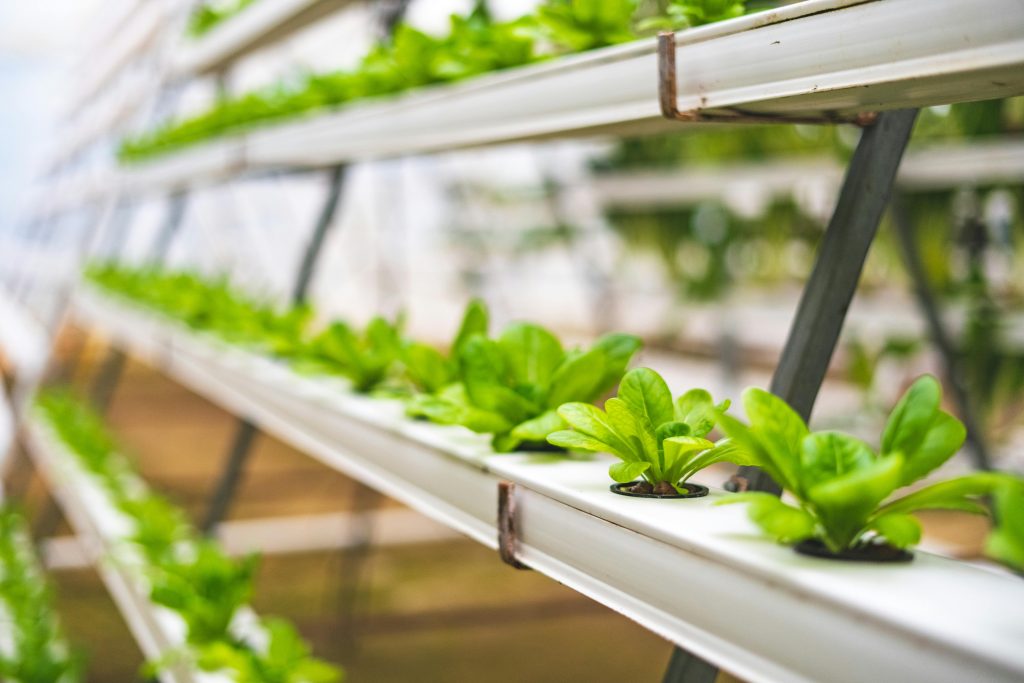

Lower Pest and Disease Pressure
Reduced Exposure to Pathogens
Hydroponic systems offer a significant advantage in terms of pest and disease management. By growing plants in a controlled environment, hydroponics reduces the exposure to external pathogens and pests. The absence of soil-borne diseases and the controlled climate prevent the entry of harmful organisms, minimizing the risk of pest infestations and disease outbreaks. This reduced exposure to pathogens contributes to healthier and more productive plants.
Isolation from External Pest Pressure
Hydroponic farming provides a physical barrier against pests by isolating plants from external insect pests and animals. With proper climate control and the use of physical barriers, hydroponic systems can prevent the entry of pests, creating an environment where crops can grow undisturbed. This isolation from external pest pressure reduces the need for chemical pesticides and promotes a more sustainable approach to crop protection.
Easier Pest and Disease Management
Managing pests and diseases is more streamlined in hydroponic systems compared to traditional farming methods. Since plants are grown in a controlled environment and closely monitored, any signs of pest infestation or disease can be identified early. This early detection allows for prompt and targeted intervention, whether it be through biological control methods or selective pesticide treatments. The ease of pest and disease management in hydroponics minimizes crop losses and ensures healthier, higher-yielding plants.
Energy Efficiency
Artificial Lighting Optimization
Hydroponic farming often utilizes artificial lighting to supplement or replace natural sunlight. By carefully optimizing lighting systems, growers can provide the necessary light spectrum and intensity for plant growth, promoting maximum photosynthesis efficiency. LED lighting, in particular, is widely used in hydroponics due to its energy efficiency and ability to provide specific light wavelengths needed for different plant stages. This energy-efficient approach to lighting minimizes energy consumption and allows for year-round crop production.
Controlled Temperature and Humidity
In hydroponic systems, temperature and humidity levels can be precisely controlled to create the ideal growing conditions for plants. By using energy-efficient heating, ventilation, and cooling systems, farmers can maintain optimal temperature and humidity ranges throughout the year. This control over environmental factors ensures that crops are not subjected to extreme conditions, promoting healthy growth and reducing energy waste.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Hydroponic farming offers the opportunity to integrate with renewable energy sources, further enhancing its energy efficiency. Solar panels can be installed to generate electricity for lighting, heating, and other energy-intensive components of the system. By harnessing renewable energy, hydroponic farms can reduce their carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural practice.
Improved Crop Quality
Consistent Production Standards
Hydroponic farming allows for consistent production standards, ensuring that crops meet high-quality requirements. By controlling the growing environment and optimizing plant nutrition, farmers can produce crops with consistent color, size, and taste. This consistency is particularly valuable for commercial growers who aim to supply high-quality produce to meet consumer demands consistently.
Enhanced Nutritional Content
Studies have shown that hydroponically grown plants can have higher nutritional content compared to conventionally grown plants. With precise control over nutrient delivery, hydroponic systems can optimize the nutrient composition, resulting in crops with increased levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This enhanced nutritional content provides consumers with more nutrient-rich food options.
Reduced Contamination Risks
Hydroponic farming reduces the risk of crop contamination compared to traditional farming practices. With the absence of soil, the potential for soil-borne pathogens, heavy metal contamination, and pesticide residues is significantly diminished. Additionally, the closed-loop water system in hydroponics minimizes the risk of water-borne contaminants. This reduction in contamination risks ensures safer and healthier food production for consumers.
Technological Advancements
Automation and Robotics
Hydroponic farming is well-suited for automation and robotics, enabling increased efficiency and productivity. Tasks such as seed planting, nutrient monitoring, and harvesting can be automated, reducing labor costs and streamlining operations. Robots equipped with sophisticated imaging systems can monitor plant health, detect pests or diseases, and provide data-driven insights for proactive plant management. These technological advancements in automation contribute to the overall sustainability and profitability of hydroponic farming.
Data-driven Decision Making
Hydroponic systems generate vast amounts of data on plant growth, nutrient levels, climate conditions, and crop performance. This data can be collected and analyzed to make informed decisions regarding plant nutrition, environmental control, and overall farm management. By leveraging data analysis tools and implementing precision agriculture techniques, hydroponic farmers can optimize their operations and maximize crop yields. Data-driven decision making allows for continuous improvement and fine-tuning of farming practices.
Precision Agriculture
Hydroponic farming is at the forefront of precision agriculture, where technology and data are utilized to optimize every aspect of the farming process. With sensors, monitoring systems, and precise control mechanisms, hydroponic farmers can monitor and adjust various parameters in real-time. This fine-grained control ensures that plants receive the exact inputs they need at the right time, leading to optimal growth, reduced resource wastage, and increased crop yields. Precision agriculture techniques enable hydroponic farmers to operate with greater efficiency and sustainability.
In conclusion, hydroponic farming offers a wide range of benefits that contribute to increased crop yield, water efficiency, reduced space requirements, elimination of soil-related issues, precise control over nutrient balance, reduction in chemical usage, lower pest and disease pressure, energy efficiency, improved crop quality, and technological advancements. By harnessing the advantages of hydroponics, farmers can overcome various challenges faced in traditional agriculture and embrace a more sustainable and productive approach to food production. With its ability to revolutionize farming practices, hydroponics has the potential to play a significant role in ensuring food security for a growing global population while minimizing environmental impacts.








