Are you looking for a more sustainable and efficient way to grow your own food? Look no further than hydroponic gardening! Hydroponics is a revolutionary method of cultivation that eliminates the need for soil, using only nutrient-rich water to nourish your plants. This innovative approach allows for faster growth, increased crop yields, and requires significantly less water compared to traditional gardening methods. With hydroponic gardening, you can enjoy fresh, organic produce while reducing your environmental footprint. So why not give it a try and embark on a journey towards sustainable food production?

What is Hydroponic Gardening?
Hydroponic gardening is a method of growing plants without the use of traditional soil. Instead, plants are cultivated in a nutrient-rich water solution that provides all the essential elements they need to thrive. This innovative approach to gardening has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its numerous benefits, including efficient water usage, maximized crop yield, and reduced pest risks.
Definition
Hydroponic gardening, also known as soilless cultivation, involves growing plants in a controlled environment using a variety of systems and techniques. By providing the plants with the necessary nutrients in a water solution, hydroponics eliminates the need for soil and enables plants to absorb nutrients more efficiently.
History
The practice of hydroponic gardening dates back to ancient times, with the Hanging Gardens of Babylon being one of the earliest examples of this cultivation method. However, it wasn’t until the 19th century that modern hydroponic techniques began to emerge. Since then, hydroponics has continued to evolve, and today it is widely used in both commercial agriculture and home gardening.
Benefits
Hydroponic gardening offers a range of benefits that make it an attractive option for sustainable food production. One of the main advantages is water conservation. By utilizing a closed-loop system and recycling water, hydroponics can significantly reduce water usage compared to conventional farming methods.
Additionally, hydroponic systems allow for maximized crop yield. Plants grown hydroponically receive the nutrients they need in precise proportions, resulting in healthier and more productive crops. Moreover, the controlled environment of hydroponics enables faster plant growth, allowing for quicker harvests and increased productivity.
Another key benefit of hydroponics is year-round cultivation. With hydroponics, you are not dependent on the seasons or climate conditions, meaning you can grow crops throughout the year, regardless of the outside conditions. This provides a stable and reliable food supply, especially in regions with limited agricultural land or extreme weather patterns.
Hydroponics also minimizes the use of soil. This is particularly advantageous in urban environments where arable land is scarce. By growing plants without soil, hydroponics opens up opportunities for gardening in areas where traditional gardening methods may be impractical or impossible.
Furthermore, hydroponic gardening reduces the risks of pests and diseases. Without soil, many common pests and pathogens are less likely to thrive, minimizing the need for chemical pesticides and fungicides. This makes hydroponics a more environmentally friendly and sustainable approach to gardening.
Components of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems consist of various components that work together to create an ideal growing environment for plants.
Reservoir
The reservoir is a container that holds the nutrient solution and provides a constant supply of water to the plants. It should be properly sized to accommodate the number of plants being grown and adequately sealed to prevent leaks or contamination.
Pump
A pump is used to circulate the nutrient solution from the reservoir to the plants. It ensures that the plants receive a continuous supply of nutrients and oxygen, promoting healthy growth.
Grow Tray
The grow tray, also known as the plant bed, is where the plants are placed. It can be made of various materials, such as plastic or metal, and should be designed to allow proper drainage and prevent waterlogging.
Growing Medium
The growing medium serves as a support structure for the plants’ roots. It can be a substance like perlite, vermiculite, coconut coir, or rockwool. The growing medium helps hold the plants in place while also providing aeration and moisture retention.
Nutrient Solution
The nutrient solution is a crucial component of hydroponic systems as it provides the essential elements the plants need to grow. It typically consists of a carefully balanced mixture of macro and micronutrients that can be adjusted to meet the specific requirements of different plant species.
pH Balancing
Maintaining the correct pH level is vital for successful hydroponic gardening. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic environment, around pH 5.5 to 6.5. pH balancing solutions or pH meters can be used to monitor and adjust the pH of the nutrient solution to ensure optimal nutrient uptake by the plants.
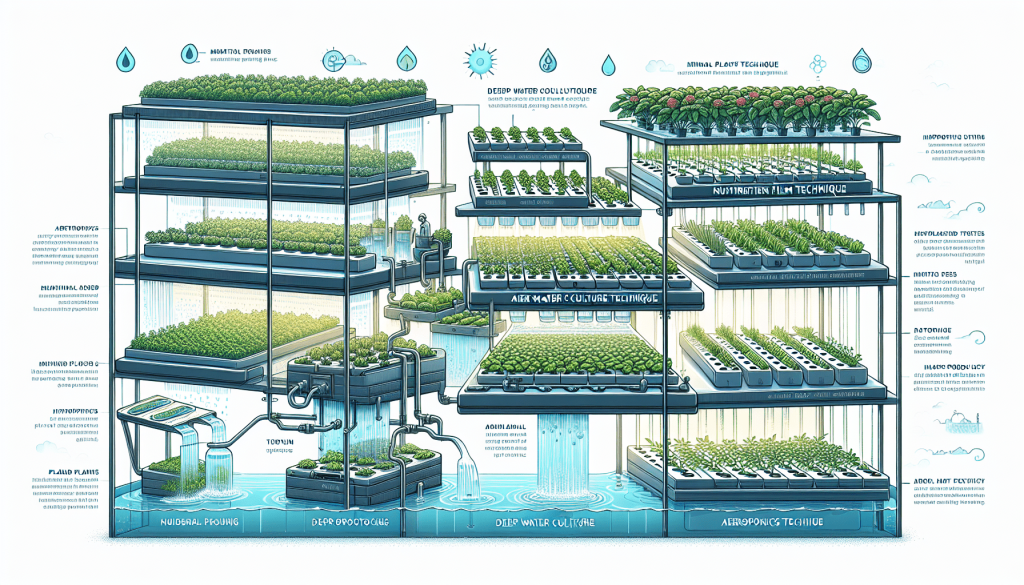
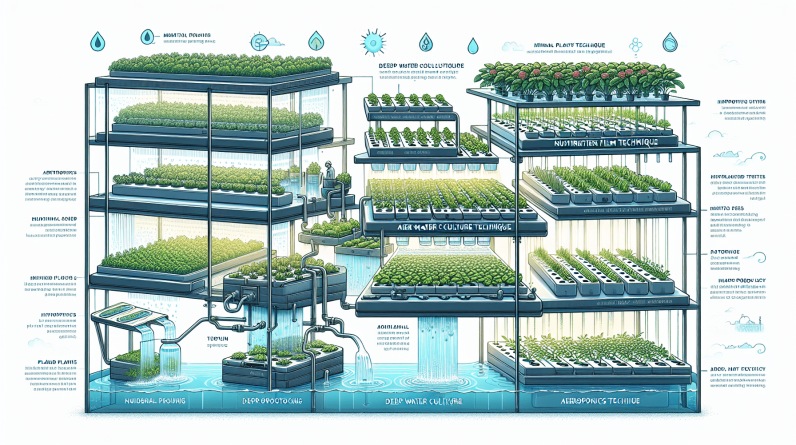
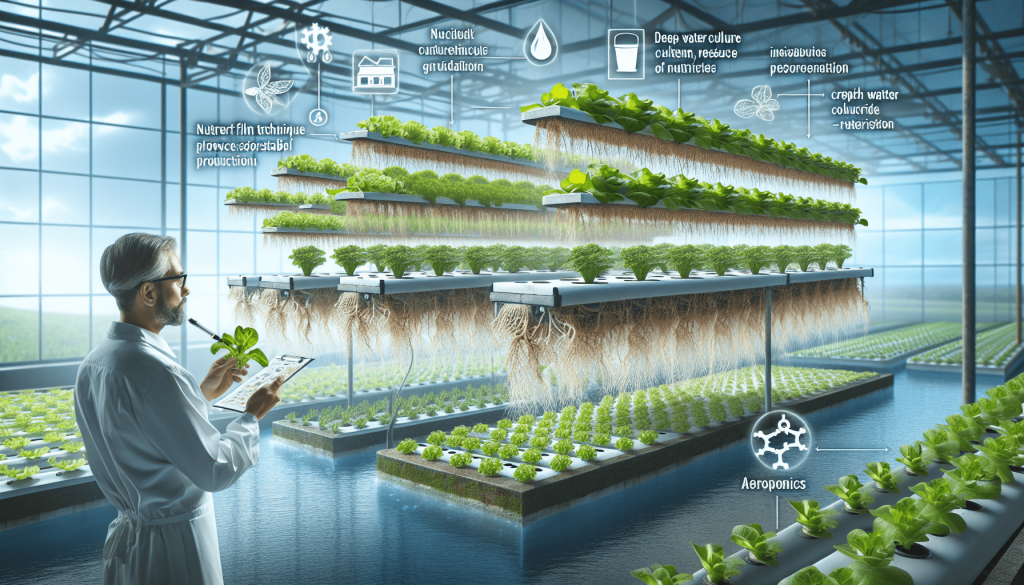
Types of Hydroponic Systems
There are several different types of hydroponic systems, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. The choice of system depends on factors such as space availability, desired crop types, and personal preference.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
In the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) system, a thin film of nutrient solution continuously flows over the plant roots, providing them with the necessary nutrients. The excess solution is then collected and recirculated back into the system. NFT systems are ideal for growing leafy greens and herbs and are known for their water efficiency.
Drip System
Drip systems are one of the most widely used hydroponic systems. In this type of system, a drip line delivers a controlled amount of nutrient solution to each plant. The solution drips onto the growing medium or root zone, ensuring the plants receive the necessary nutrients while minimizing water wastage.
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
Ebb and Flow systems work by flooding the grow tray with the nutrient solution and then draining it back into the reservoir. This flooding and draining cycle is typically automated through a timer or sensor. This type of system is versatile and suitable for a wide range of plants.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture systems suspend the plants’ roots directly in the nutrient solution, allowing for maximum oxygenation. The roots are typically held in place by a floating platform or net pots. DWC systems are popular for their simplicity and are often used for growing larger plants like tomatoes or peppers.
Aeroponics
Aeroponic systems involve suspending the plant roots in mid-air and misting them with a nutrient solution. This mist provides both nutrients and oxygen directly to the roots. Aeroponics is considered one of the most efficient methods of hydroponic gardening and is frequently used for growing high-value crops with delicate root systems.
Advantages of Hydroponic Gardening
Hydroponic gardening offers numerous advantages that make it an appealing choice for both home gardeners and commercial growers.
Water Conservation
One of the primary benefits of hydroponics is its efficient use of water. Compared to traditional soil-based gardening, hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water. This is because hydroponics recirculates and reuses the water, reducing wastage and preserving this precious resource.
Maximized Crop Yield
Hydroponic systems are designed to provide plants with optimal growing conditions, leading to higher crop yields compared to conventional methods. By providing a precisely balanced nutrient solution, controlling environmental factors like humidity and temperature, and utilizing efficient growing techniques, hydroponic gardening can produce larger, healthier, and more abundant crops.
Faster Growth Rate
Plants grown hydroponically typically experience faster growth rates compared to those grown in soil. This is due to the plants’ efficient uptake of nutrients, constant access to water and oxygen, and elimination of competition with surrounding plants. The accelerated growth also means crops can be harvested sooner, allowing for multiple harvests throughout the year.
Year-round Cultivation
One of the significant advantages of hydroponic gardening is the ability to grow crops all year round, regardless of the external climate. By providing a controlled environment with optimal light, temperature, and humidity levels, hydroponics enables continuous cultivation, ensuring a steady supply of fresh produce regardless of the season.
Minimized Use of Soil
Hydroponics eliminates the need for large plots of arable land, making it a suitable option for urban areas or regions with limited access to fertile soil. This allows individuals to grow their food in small spaces like balconies or rooftops and makes it possible to cultivate crops in areas where the soil may be contaminated or unsuitable for traditional gardening.
Reduced Pest and Disease Risks
Without soil, many pests, diseases, and weeds that commonly afflict traditional gardens are less prevalent in hydroponic systems. The absence of soil-borne pathogens reduces the risk of diseases, while the controlled environment and isolation from external pests provide a protective barrier. This reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides and promotes healthier, chemical-free produce.

Challenges of Hydroponic Gardening
While hydroponic gardening offers many advantages, it also presents some challenges that need to be addressed to ensure successful cultivation.
Initial Setup Costs
Setting up a hydroponic system can be more expensive initially compared to traditional gardening methods. The cost of purchasing the necessary equipment, such as pumps, grow trays, lighting systems, and nutrient solutions, can be a significant investment. However, with proper planning and research, these costs can be mitigated, and long-term savings can be achieved through increased crop yield and reduced water usage.
Technical Knowledge and Maintenance
Hydroponic gardening requires a certain level of technical know-how. Understanding the specific nutrient needs of different plants, monitoring pH levels, and maintaining proper water and nutrient balance can be challenging, especially for beginners. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and ensuring proper system functionality, is also necessary to prevent issues like clogging or nutrient imbalances.
Monitoring and Adjusting Nutrient Levels
Maintaining the correct nutrient levels in hydroponic systems is crucial for plant health and growth. Regular monitoring of nutrient levels, as well as adjusting the solution to meet the changing needs of plants, is necessary to prevent deficiencies or excesses. This requires a comprehensive understanding of plant nutrition and periodic testing of the nutrient solution.
Power Dependency
Most hydroponic systems rely on electrical pumps, lighting, and timers. This power dependency may pose a challenge in certain situations, such as power outages or remote locations without access to reliable electricity. Backup power sources or alternative energy solutions can be employed to mitigate these challenges.
Suitable Crops for Hydroponic Gardening
Hydroponic systems are suitable for growing a wide range of crops, but some plant varieties thrive particularly well in this soilless environment.
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are well-suited for hydroponic gardening. They have shallow root systems that make them compatible with various hydroponic systems, and they have a relatively short growth cycle, allowing for quicker harvests.
Herbs
Herbs like basil, parsley, cilantro, and mint are popular choices for hydroponic gardening due to their compact size, high demand, and ability to flourish in controlled environments. Growing herbs hydroponically allows for consistent harvests, flavorful leaves, and extended growing seasons.
Strawberries
Strawberries are also well-suited for hydroponic cultivation. The hanging root system of strawberries makes them ideal for vertical growing systems and hanging baskets. Hydroponic strawberries often produce larger and sweeter fruits, with fewer pest issues compared to traditional soil-based methods.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a staple in many gardens, and hydroponics offers an excellent way to cultivate them. With their deep root systems, tomatoes can thrive in larger hydroponic systems like deep water culture (DWC) or ebb and flow setups. Hydroponically grown tomatoes tend to have higher yields and better fruit quality.
Peppers
Peppers, whether bell peppers or chili peppers, can also be successfully grown hydroponically. They require similar conditions as tomatoes and can be grown in similar systems. Hydroponic peppers often produce more abundant and faster harvests, and the controlled environment helps maximize their flavor and size.
Cucumbers
Cucumbers are known for their vigorous growth and relatively high water requirements, making them an excellent choice for hydroponic gardening. With the right trellising or support system, cucumbers can thrive in hydroponic setups like NFT or drip systems. Hydroponically grown cucumbers tend to have a sweeter taste and superior texture.

Nutrient Solutions in Hydroponics
Nutrient solutions play a crucial role in hydroponic gardening, providing plants with the essential elements they need for growth and development.
Macro and Micronutrients
Macronutrients, including nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S), are required in larger quantities by plants. These nutrients are involved in various processes, such as leaf development, root growth, and flower and fruit production.
Micronutrients, on the other hand, are required in smaller quantities but are equally essential. These include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), boron (B), and chlorine (Cl). Micronutrients are involved in enzyme activation, photosynthesis, and other metabolic functions.
Determining Nutrient Requirements
Different plant species have varying nutrient requirements, and it is essential to provide the correct balance of nutrients to achieve optimal growth. Nutrient requirements can vary based on factors such as plant stage (vegetative versus flowering), crop type, and environmental conditions. Conducting regular water and soil tests as well as observing plant symptoms can help determine nutrient deficiencies or excesses.
Prepared Nutrient Solutions vs. DIY
In hydroponic gardening, nutrient solutions can be prepared using commercial hydroponic fertilizers or by mixing individual nutrient salts. Prepared nutrient solutions are convenient and provide a balanced mix of macro and micronutrients. However, some hydroponic gardeners prefer DIY nutrient solutions to have more control over the specific nutrient composition and to experiment with different formulations. DIY nutrient solutions require careful calculations and precise measurements to ensure the correct nutrient balance.
Hydroponic Gardening at Home
Hydroponic gardening is not limited to large-scale commercial operations. It can also be practiced in a home setting, allowing individuals to grow their own fresh produce in a controlled environment.
Setting up a Home Hydroponic System
To set up a home hydroponic system, several key considerations must be taken into account. These include the available space, budget, desired crop types, and technical expertise. Home hydroponic setups can range from small-scale systems like countertop herb gardens to larger setups using spare rooms or greenhouses.
Choosing the Right Location
When setting up a home hydroponic system, it is crucial to choose the right location. The chosen area should have access to natural or artificial light, proper ventilation, and easy access to water and electricity. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and the available space should also be considered to create an optimal growing environment.
Selecting Crops for Home Hydroponics
Home hydroponic systems are versatile and can accommodate a variety of crops. When choosing crops for home hydroponics, consider the available space, lighting conditions, and personal preferences. Herbs, leafy greens, strawberries, and compact vegetables like cherry tomatoes and peppers are popular choices due to their relatively small size and suitability for hydroponic cultivation.

Hydroponic Gardening in Commercial Settings
Hydroponic gardening is not limited to small-scale home setups. It has gained significant traction in large-scale commercial operations, offering sustainable and innovative approaches to food production.
Large-scale Production
Hydroponics allows for efficient use of space and resources, making it well-suited for large-scale food production. High-tech commercial hydroponic systems can be designed to maximize productivity per square footage, ensuring optimal space utilization and cost-effectiveness. These large-scale operations make it possible to supply fresh produce to local markets year-round, reducing dependence on long-distance transportation and improving overall food security.
Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is a form of hydroponic gardening that involves cultivating crops in stacked layers or vertically oriented structures. By utilizing vertical space, multi-level growing systems can be established, making it possible to grow large quantities of crops in compact urban areas. Vertical farming offers significant opportunities for urban agriculture, reducing the need for extensive farmland and minimizing environmental impact.
Integration with Aquaculture
Hydroponic systems can be integrated with aquaculture through a process known as aquaponics. Aquaponics combines hydroponics and fish farming, creating a mutually beneficial system. Fish waste provides nutrients for hydroponic plants, while the plants filter and purify the water for the fish. This integration of aquaculture and hydroponics offers a sustainable and symbiotic approach to food production, enhancing resource efficiency and minimizing waste.
Conclusion
Hydroponic gardening presents an innovative and sustainable solution for food production. Through the use of nutrient-rich water solutions, efficient water usage, and controlled environments, hydroponics offers numerous benefits, including maximized crop yield, faster growth rates, year-round cultivation, and reduced reliance on soil. While there are some challenges to consider, such as setup costs and technical knowledge requirements, the advantages of hydroponic gardening make it a compelling option for both home gardeners and commercial growers. With the versatility to grow a wide range of crops and the potential for vertical farming and aquaponics integration, hydroponics paves the way for a more sustainable and efficient future of agriculture.