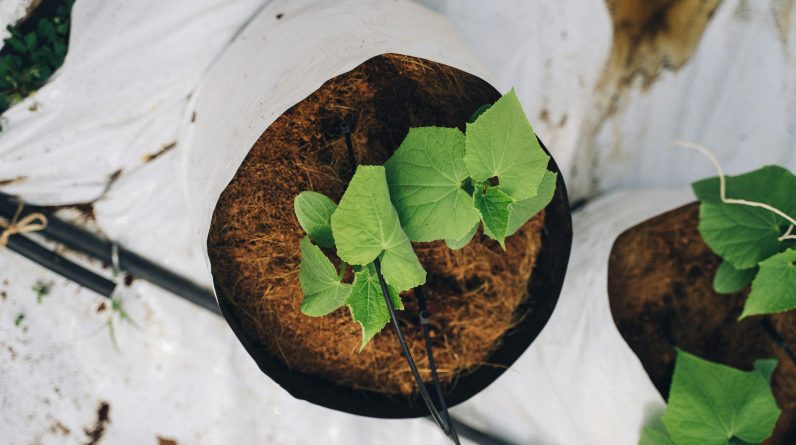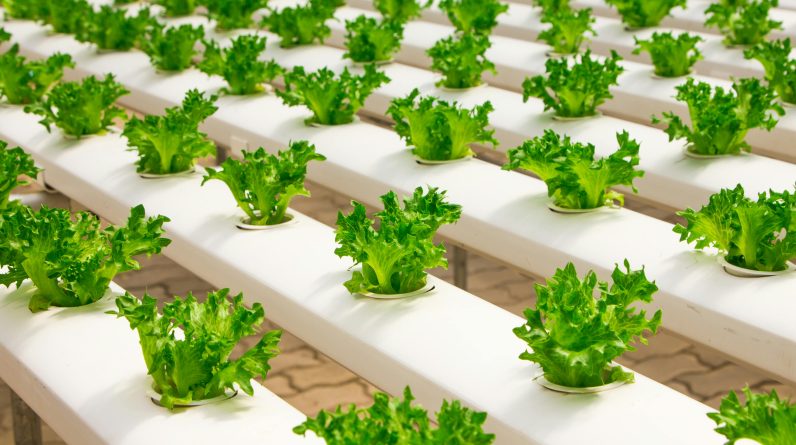
Imagine a world where lush green vegetables can be grown without the need for soil. Sounds intriguing, doesn’t it? Well, this is exactly what hydroponic growing systems offer. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of hydroponics and compare it to traditional soil farming. From the advantages of hydroponics to the drawbacks of soil farming, we’ll uncover the similarities and differences between these two methods of cultivation. So, get ready to dive into the world of sustainable and innovative farming techniques.

Hydroponic Growing System
Definition and Basics
A hydroponic growing system is a method of cultivating plants without using soil. Instead, the plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution that provides all the necessary elements for their growth. This system relies on the use of a variety of growing mediums, such as perlite, coco coir, or clay pellets, to support the plants and hold them in place. The water solution is continuously circulated, ensuring that the plants receive a constant supply of nutrients and water.
Advantages
There are several advantages to using a hydroponic growing system. Firstly, it allows for greater control over the growing conditions, including temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels. This ensures optimal conditions for plant growth, resulting in healthier and more productive crops. Additionally, hydroponic systems use less water than traditional soil farming methods since the water is recirculated and not lost through evaporation or runoff. This makes hydroponics a more environmentally-friendly option.
Another advantage of hydroponic systems is their space efficiency. Since the plants are grown in a controlled environment and do not rely on expansive fields, they can be grown in smaller spaces. This is particularly beneficial in urban areas where land is limited. Additionally, the absence of soil eliminates the need for tilling and weeding, reducing labor and maintenance requirements.
Disadvantages
While hydroponic growing systems offer numerous benefits, there are also some disadvantages to consider. One of the biggest challenges is the initial cost of setting up a hydroponic system. The equipment required, such as pumps, timers, and grow lights, can be expensive. Additionally, there is a learning curve associated with hydroponics, as it requires knowledge and understanding of the system’s mechanics, nutrient requirements, and pH levels. This may deter some individuals from adopting this method of farming.
Another potential drawback is the reliance on a constant supply of electricity for the equipment to function properly. In the event of a power outage or equipment failure, the plants may suffer. Additionally, the lack of any soil-based buffer can make hydroponic plants more susceptible to sudden changes in nutrient levels or pH, which can negatively impact their growth if not closely monitored and adjusted.
Traditional Soil Farming
Definition and Basics
Traditional soil farming, also known as conventional farming, is the age-old method of cultivating plants in the ground. It involves preparing the soil by tilling and adding organic matter, such as compost or manure, to enrich its nutrient content. Seeds or seedlings are then planted directly into the soil, taking advantage of the natural ecosystem and soil biology to support plant growth.
Advantages
Traditional soil farming has been the backbone of agriculture for centuries, and it offers several advantages. One of the primary benefits is the lower initial cost compared to setting up a hydroponic system. Traditional farming does not require specialized equipment or high-tech infrastructure, making it accessible to a wider range of farmers. Additionally, traditional farming methods are more familiar and less complicated, making it easier for individuals with limited agricultural experience to start their own farms.
Another advantage is the natural balance of nutrients and microorganisms present in the soil. The complex ecosystem of soil provides a diverse array of natural resources that contribute to plant health and growth. This can result in improved flavor and nutritional content of crops, making them more appealing to consumers. Additionally, traditional farming practices can help to promote soil health and regeneration, which is vital for long-term agricultural sustainability.
Disadvantages
Despite its long-standing history, traditional soil farming also has its disadvantages. One major challenge is water usage. Traditional farming methods often rely on rainfall or irrigation, which can lead to water wastage through runoff. Moreover, it can be difficult to control the amount of water each plant receives, potentially leading to overwatering or underwatering. This inefficiency in water use can be detrimental, particularly in regions where water scarcity is a concern.
Space efficiency is another aspect where traditional soil farming falls short. Conventional farms typically require large areas of land to accommodate crops. This limits their viability in urban areas or regions with limited available land. Furthermore, the reliance on soil can lead to issues such as erosion, soil compaction, and nutrient depletion over time. These problems require additional interventions, such as crop rotation or soil amendments, to maintain soil health and ensure productive harvests.
Comparison Factors
Water Usage
When comparing hydroponic growing systems to traditional soil farming, water usage is a critical factor to consider. In hydroponics, water usage is significantly reduced since the water is recirculated within the system. This closed-loop system minimizes water loss due to evaporation or runoff, making it a highly water-efficient method of cultivation. Traditional farming methods, on the other hand, often rely on irrigation or rainfall, which can lead to water wastage through runoff or evaporation. Therefore, in terms of water usage, hydroponic systems have a clear advantage.
Nutrient Control
Nutrient control is another crucial aspect to compare between hydroponic growing systems and traditional soil farming. In hydroponics, the nutrient solution is carefully formulated to provide the plants with an optimal balance of nutrients for their growth. This allows for precise control over nutrient uptake and ensures that the plants receive all the essential elements they need. In traditional soil farming, the nutrient content and composition of the soil can vary significantly depending on factors such as soil type, organic matter, and previous cropping history. While soil amendments can be added, it is more challenging to achieve the same level of nutrient control as in hydroponics.
Growth Rate
The growth rate of plants is an essential factor to consider when comparing hydroponic growing systems to traditional soil farming. In hydroponics, the plants are provided with a constant supply of nutrients and water, which promotes rapid and robust growth. The controlled environment and optimized conditions further enhance plant development, resulting in quicker maturation and higher yields. Traditional soil farming, however, may have more variable growth rates depending on factors such as soil quality, weather conditions, and pest or disease pressures. While some crops may thrive in soil-based systems, others may face challenges that hinder their growth rate and overall productivity.
Space Efficiency
Space efficiency is a significant advantage of hydroponic growing systems. Since hydroponic plants do not rely on expansive fields, they can be grown in smaller spaces. This is particularly advantageous in urban areas where available land is limited. Vertical hydroponic systems, such as tower gardens or vertical racks, maximize space utilization by allowing plants to grow upwards. Traditional soil farming, on the other hand, requires larger areas of land to accommodate crops. As a result, hydroponics offer a more space-efficient solution for agricultural production.
Environmental Impact
When comparing the environmental impact of hydroponic growing systems to traditional soil farming, several factors come into play. Hydroponics, due to its closed-loop system and efficient use of resources, generally has a lower environmental impact. The reduced water usage and controlled nutrient application help to minimize the potential for water pollution or nutrient runoff. Additionally, the absence of chemical pesticides or fertilizers in hydroponics can contribute to a healthier ecosystem and reduce the risk of groundwater contamination. Traditional soil farming, on the other hand, may have a greater environmental impact due to potential soil erosion, nutrient leaching, and the use of chemical inputs.
Water Usage
Hydroponic Growing System
One of the significant advantages of a hydroponic growing system is its efficient use of water. In hydroponics, water is recirculated within the system, resulting in minimal water loss. This closed-loop approach reduces water consumption significantly compared to traditional soil farming. Water is delivered directly to the roots of the plants, ensuring maximum absorption and minimizing waste. Additionally, hydroponic systems can be equipped with sensors or timers to regulate water usage and prevent overwatering.
Traditional Soil Farming
Traditional soil farming often relies on irrigation or rainfall for water supply. However, a substantial amount of water is lost through evaporation, runoff, or deep percolation, particularly in regions with sandy or porous soils. This inefficiency in water usage can lead to water scarcity issues and environmental concerns. Irrigation systems used in traditional soil farming need to be carefully managed to ensure water is utilized efficiently. Improper irrigation practices can result in water wastage, increased energy costs, and negative impacts on water resources.

Nutrient Control
Hydroponic Growing System
Nutrient control is a significant advantage of hydroponic growing systems. In a hydroponic setup, the nutrient solution is carefully formulated to provide the plants with a precise balance of all the necessary elements for their growth. This allows for optimal nutrient uptake and eliminates the risk of nutrient deficiencies or imbalances. The composition of the nutrient solution can be adjusted based on the specific needs of different plants or growth stages. The controlled environment of hydroponics ensures that plants receive the exact nutrients they require for healthy development.
Traditional Soil Farming
In traditional soil farming, nutrient control can be more challenging. Soil composition varies across different regions, and its nutrient content may not always align with the specific needs of the plants being grown. Soil amendments, such as compost or fertilizers, are typically added to supplement the nutrient levels. However, achieving precise nutrient control in soil can be challenging, as factors such as nutrient availability, soil moisture, and pH can impact nutrient uptake. Soil testing and analysis are often required to determine the appropriate amendments for optimal plant growth.
Growth Rate
Hydroponic Growing System
Hydroponic growing systems offer several advantages when it comes to plant growth rate. The controlled environment and optimized conditions in hydroponics result in rapid and consistent plant growth. The plants receive a constant supply of nutrients and water, allowing them to focus their energy on vegetative growth and fruiting. This controlled environment also helps to protect the plants from external factors such as pests, diseases, or adverse weather conditions, further enhancing their growth rate.
Traditional Soil Farming
The growth rate of plants in traditional soil farming can be influenced by various factors. Soil quality, weather conditions, and pest or disease pressures can all impact plant growth. While some crops may thrive in soil-based systems, others may face challenges that hinder their growth rate. Additionally, traditional farming methods often rely on seasonal cycles and natural growth patterns, resulting in more variable growth rates compared to hydroponic systems. Dependence on external factors and limited control over growing conditions can affect the overall growth rate in traditional soil farming.
Space Efficiency
Hydroponic Growing System
Hydroponic growing systems are highly efficient in terms of space utilization. The absence of soil allows plants to be grown closer together, maximizing the use of available space. Vertical hydroponic systems, such as tower gardens or vertical racks, take this efficiency to another level by enabling plants to grow upwards, further optimizing space utilization. This makes hydroponics particularly suitable for urban areas or regions with limited land availability.
Traditional Soil Farming
Traditional soil farming requires larger areas of land to accommodate crops. Depending on the type of crop and recommended spacing, soil-based farming often demands significant land resources. The need for field rotation and considerations for plant health and disease prevention can further impact the spatial requirements. This can limit the suitability of traditional soil farming in areas with limited available land, making it less space-efficient compared to hydroponics.
Environmental Impact
Hydroponic Growing System
Hydroponic growing systems generally have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional soil farming. The closed-loop system of hydroponics reduces water consumption and minimizes the potential for water pollution or nutrient runoff. The absence of chemical pesticides or fertilizers in hydroponics also contributes to a healthier ecosystem and reduces the risk of groundwater contamination. Additionally, hydroponic systems can be designed to consume less energy through the use of energy-efficient lighting and equipment.
Traditional Soil Farming
Traditional soil farming can have a greater environmental impact due to various factors. Soil erosion, nutrient leaching, and pesticide runoff are common concerns associated with traditional farming practices. Erosion can lead to the loss of fertile topsoil, reducing the productivity of the land and negatively impacting the environment. The use of chemical inputs, such as synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, can also have adverse effects on water quality and ecosystem health. Soil conservation practices and sustainable agricultural techniques are essential to mitigate and minimize the environmental impact of traditional soil farming.

Conclusion
Hydroponic growing systems and traditional soil farming each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Hydroponics offer precise control over growing conditions, efficient water usage, and faster growth rates. They are also more space-efficient and have a lower environmental impact. However, the initial cost and learning curve associated with hydroponics can be deterrents for some individuals.
On the other hand, traditional soil farming has the advantage of lower initial costs and a natural balance of nutrients in the soil. It also promotes soil health and supports a diverse ecosystem. However, traditional farming methods may require larger areas of land, face challenges with water usage and nutrient control, and have a greater environmental impact.
Ultimately, the choice between a hydroponic growing system and traditional soil farming depends on various factors such as available resources, location, crop selection, and personal preferences. Both methods have their merits and drawbacks, and farmers should carefully evaluate their specific needs and circumstances when deciding which approach to adopt.







