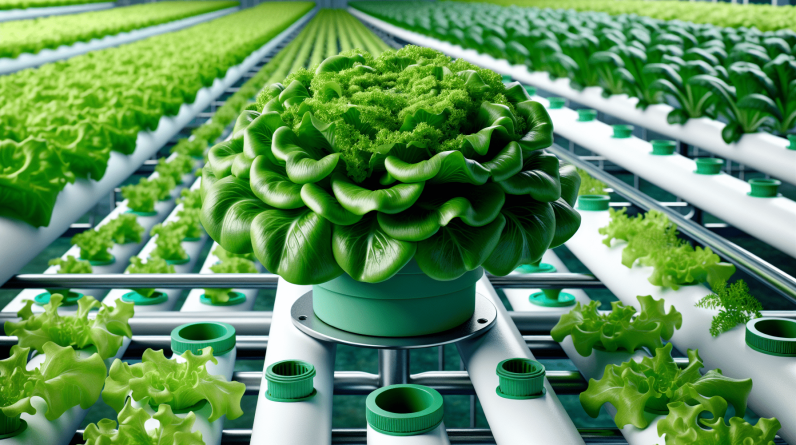
Do you want to witness a revolutionary approach to farming that could potentially transform the agriculture industry? Look no further than hydroponic farming. Utilizing a water-based system that eliminates the need for soil, this innovative method is gaining popularity worldwide for its numerous benefits. From maximizing yields to conserving water resources, hydroponic farming presents a sustainable and efficient alternative for growers. In this article, explore the seven key advantages of hydroponic farming and discover why it is becoming a game-changer in the quest for sustainable food production.

Increased Crop Yield
Optimized Nutrient Delivery
In hydroponic farming, plants are supplied with all the essential nutrients they need directly through the water solution. This allows for precise control over nutrient levels, ensuring that plants receive the optimal amount of each nutrient for their growth and development. The absence of soil also eliminates the risk of nutrient depletion, as all the necessary nutrients are readily available to the plants. This optimized nutrient delivery system results in increased crop yield, as plants are able to grow faster and produce larger and healthier fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
Consistent Growing Conditions
One of the key advantages of hydroponic farming is the ability to create consistent growing conditions for plants. In traditional soil-based agriculture, plants are subject to the whims of nature, with unpredictable weather patterns and varying soil quality. However, in hydroponics, the entire growing environment can be carefully controlled. Factors such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and pH levels can be adjusted to create the ideal conditions for plant growth. This consistency in growing conditions promotes uniform growth among plants, leading to increased crop yield and higher quality produce.
Year-Round Production
Hydroponic farming enables year-round production, regardless of the external climate conditions. By creating an indoor growing environment, farmers can overcome the limitations of seasonal changes and grow crops throughout the year. This not only ensures a steady supply of fresh produce but also allows farmers to meet the demands of the market consistently. With hydroponics, you can enjoy fresh fruits, vegetables, and herbs, even during the winter months when traditional farming is not possible.
Water Conservation
Significantly Reduced Water Usage
Water scarcity is a pressing issue in many parts of the world, and traditional agriculture is known to be a significant water consumer. However, hydroponic farming has the potential to revolutionize water usage in agriculture. Compared to soil-based farming, hydroponics requires significantly less water to grow crops. The water used in the system is circulated and recycled, minimizing wastage. Additionally, with the absence of soil, there is no water loss through evaporation or infiltration. This water conservation aspect of hydroponics not only helps address the global water crisis but also reduces the burden on farmers to access and supply large quantities of water.
Prevention of Water Contamination
Another benefit of hydroponic farming is the prevention of water contamination. In traditional agriculture, excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides can lead to runoff, which contaminates nearby water sources. This can have detrimental effects on the environment and human health. However, in hydroponics, fertilizers and nutrients are directly supplied to the plants through the water solution, eliminating the risk of runoff contamination. This makes hydroponics a more environmentally-friendly and sustainable farming method, ensuring that our water sources remain clean and safe.
Efficient Nutrient Management
Precise Control over Nutrient Levels
Hydroponic farming offers precise control over nutrient levels, allowing farmers to tailor the nutrient solution to the specific needs of each plant. By monitoring and adjusting the nutrient levels, plants receive the optimal balance of nutrients required for their growth and development. This precision in nutrient management promotes healthier plants, faster growth, and improved overall crop yield. Furthermore, it minimizes the wastage of nutrients, as only the necessary amount is provided to the plants, reducing costs and environmental impact.
Minimized Nutrient Runoff
In traditional agriculture, excess nutrients applied to the soil can often result in nutrient runoff, which pollutes rivers, lakes, and other water bodies. This not only harms aquatic ecosystems but also contributes to the growth of harmful algal blooms. However, with hydroponic farming, the risk of nutrient runoff is significantly minimized. All the nutrients are supplied directly to the plants, and any excess nutrients not absorbed by the plants can be easily recirculated or properly disposed of. This environmentally-friendly approach reduces nutrient pollution and promotes sustainable farming practices.
Reduced Soil Erosion
Elimination of Soil-Based Agriculture
One of the major advantages of hydroponic farming is the elimination of soil-based agriculture. Soil erosion is a significant issue in conventional farming, where plowing, tilling, and excessive water runoff can degrade the soil structure. This not only depletes the soil of its nutrients but also leads to the loss of fertile topsoil. On the other hand, hydroponics completely bypasses the need for soil, ensuring that there is no erosion or degradation of soil. This preservation of the soil allows for greater sustainability and ensures the long-term viability of farming.
Preservation of Natural Ecosystems
By eliminating soil-based agriculture, hydroponic farming helps preserve natural ecosystems. Traditional farming practices often require the clearing of land, which can result in deforestation and habitat destruction. In contrast, hydroponics can be implemented in vertically stacked systems, utilizing urban areas or repurposing unused spaces. This efficient use of space minimizes the need for large areas of land and reduces the impact on natural habitats. By adopting hydroponics, we can ensure the protection and conservation of our valuable natural ecosystems.

Pest and Disease Control
Limited Exposure to Soil-Borne Pests
With soil-based farming, plants are exposed to a variety of pests and diseases that reside in the soil. These soil-borne pests can damage crops, leading to reduced yields and increased reliance on pesticides. However, in hydroponics, the absence of soil means that plants are not exposed to these pests. This reduces the need for pesticide application, making hydroponic farming a more environmentally-friendly and sustainable approach. By minimizing the risk of pest infestations, hydroponics helps protect crops, ensuring healthier plants and higher crop yields.
Reduced Risk of Soil-Borne Diseases
Soil-borne diseases, caused by fungi, bacteria, and other pathogens present in the soil, can have devastating effects on crops. These diseases can spread rapidly, causing widespread crop damage and economic losses for farmers. However, in hydroponic farming, the risk of soil-borne diseases is greatly reduced. By growing plants in a soil-free environment, the pathogens that cause these diseases are effectively eliminated. This allows for healthier plants and improved crop quality, minimizing the need for disease control measures and ensuring a higher success rate in crop production.
Space Optimization
Vertical Growing Systems
One of the unique aspects of hydroponics is the ability to utilize vertical growing systems. Instead of the traditional horizontal layout, hydroponic systems can be designed to stack plants vertically, maximizing the use of available space. This vertical farming technique allows for higher crop density and increased productivity per square foot. With limited land resources in urban areas, vertical growing systems offer a practical solution to grow a large quantity of crops within a smaller footprint. This innovative approach to space optimization is revolutionizing agriculture and enabling farming in areas with limited land availability.
Utilization of Urban Areas
Hydroponic farming also enables the utilization of urban areas for food production. In densely populated cities, finding adequate land for traditional agriculture is a significant challenge. However, hydroponics can be implemented in vertical farms, rooftop gardens, or indoor facilities, making use of unused spaces in urban environments. By transforming buildings into productive farms, hydroponics brings food production closer to consumers, reducing transportation costs and ensuring the availability of fresh and nutritious produce to urban populations. This integration of agriculture into cities is a step towards a more sustainable and resilient food system.
Increased Productivity per Square Foot
By adopting hydroponics, farmers can achieve higher productivity per square foot of growing area. The controlled growing environment and optimized nutrient delivery system allow plants to reach their full potential and produce more abundant harvests. Unlike in traditional agriculture, where variable growing conditions and limited access to nutrients can hinder plant growth, hydroponic farming provides the ideal conditions for plants to thrive. This increased productivity not only benefits farmers economically but also helps meet the growing demand for food sustainably.

Energy Efficiency
Reduced Energy Consumption
Hydroponic farming can be designed with energy efficiency in mind. By utilizing advanced technologies and energy-saving practices, the energy consumption of hydroponic systems can be significantly reduced. LED lights, for example, can be used for optimal energy usage in providing artificial lighting for plants. Additionally, the controlled environment in hydroponics allows for better insulation and regulates temperature and humidity, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. By prioritizing energy efficiency in hydroponic farming, farmers can minimize their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable agricultural sector.
Optimized Use of Artificial Lighting
One of the key elements of successful hydroponic farming is providing adequate lighting for plant growth. In the absence of natural sunlight, artificial lighting is used to stimulate plant photosynthesis. However, compared to traditional agriculture, hydroponics allows for the optimized use of artificial lighting. LED lights, which are energy-efficient and emit specific wavelengths of light, can be used to mimic natural sunlight and provide the ideal light spectrum for plant growth. By fine-tuning the lighting conditions, farmers can maximize the productivity and efficiency of their hydroponic systems, resulting in higher crop yields and improved energy utilization.
Reduced Chemical Dependency
Controlled Environment Limits Pesticide Use
In hydroponic farming, the controlled environment helps limit the need for pesticide application. This is because pests and diseases are less likely to thrive in the absence of soil and controlled growing conditions. As a result, hydroponic farmers can significantly reduce their dependence on chemical pesticides, making the farming process safer for both farmers and consumers. By adopting integrated pest management strategies, such as biological controls and monitoring systems, hydroponic farmers can effectively manage pests without resorting to harmful chemicals, ensuring the production of healthier and safer food.
Fewer Chemicals in Food Production
The use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in traditional agriculture can result in residual chemicals in food products, posing potential health risks. However, in hydroponic farming, where the nutrient solution and growing environment are carefully controlled, the use of chemicals can be minimized. With a focus on organic and sustainable farming practices, hydroponic systems prioritize the use of natural and safe inputs. By reducing the reliance on chemicals, hydroponics offers a healthier and more sustainable approach to food production, ensuring that the food we consume is free from harmful chemical residues.

Consistent Crop Quality
Controlled Environmental Factors
The controlled environment in hydroponic farming allows for precise control over various environmental factors that can impact crop quality. From temperature and humidity to light intensity and CO2 levels, all these factors can be carefully monitored and adjusted to create the ideal conditions for plant growth. This consistency in the growing environment ensures that plants receive the right balance of factors necessary for their development, resulting in consistent crop quality. Whether it’s leafy greens, juicy tomatoes, or flavorful herbs, hydroponic farming guarantees that every harvest is of the highest quality and meets the desired standards.
Absence of External Contaminants
In traditional agriculture, crops are often exposed to external contaminants such as dust, pollutants, and pathogens from the soil or air. These contaminants can affect the quality and safety of the produce, potentially posing health risks to consumers. However, in hydroponic farming, the absence of soil and the controlled growing environment mitigates the risk of external contamination. Plants are grown in a clean and sterile environment, reducing the likelihood of contamination by external factors. This ensures that the food produced through hydroponics is of superior quality, meeting the highest standards of food safety and consumer satisfaction.
Improved Food Safety
Hygienic Growing Conditions
Hydroponic farming offers hygienic growing conditions, minimizing the risk of foodborne illnesses. Without relying on soil, which can harbor pathogens, hydroponic systems provide a clean and controlled environment for plant growth. The absence of weeds, pests, and soil-borne diseases ensures that the crops remain free from contamination throughout the growing process. With proper sanitation practices in place, hydroponic farmers can maintain high levels of hygiene, reducing the likelihood of microbial contamination and ensuring the safety of the food they produce.
Minimized Risk of Bacterial Contamination
Bacterial contamination is a significant concern in food production, especially in crops that are consumed raw or minimally processed. In hydroponic farming, the risk of bacterial contamination is minimized, thanks to the sterile growing environment and absence of pathogens commonly found in soil. By following strict hygiene protocols and implementing quality control measures, hydroponic farmers can prevent bacterial contamination and produce safe and healthy crops. This aspect of hydroponics reassures consumers that the food they consume is less likely to cause foodborne illnesses, providing peace of mind and confidence in the safety of the produce.
In conclusion, hydroponic farming offers numerous benefits across various aspects of agriculture. From increased crop yield and water conservation to efficient nutrient management and reduced chemical dependency, hydroponics presents a sustainable and innovative solution to the challenges faced by traditional agriculture. With space optimization, energy efficiency, and improved food safety, hydroponic farming paves the way for a more resilient and sustainable food system. As we strive to meet the growing demand for food while preserving our natural resources, hydroponics emerges as an exciting and promising farming method that holds great potential for the future of agriculture.